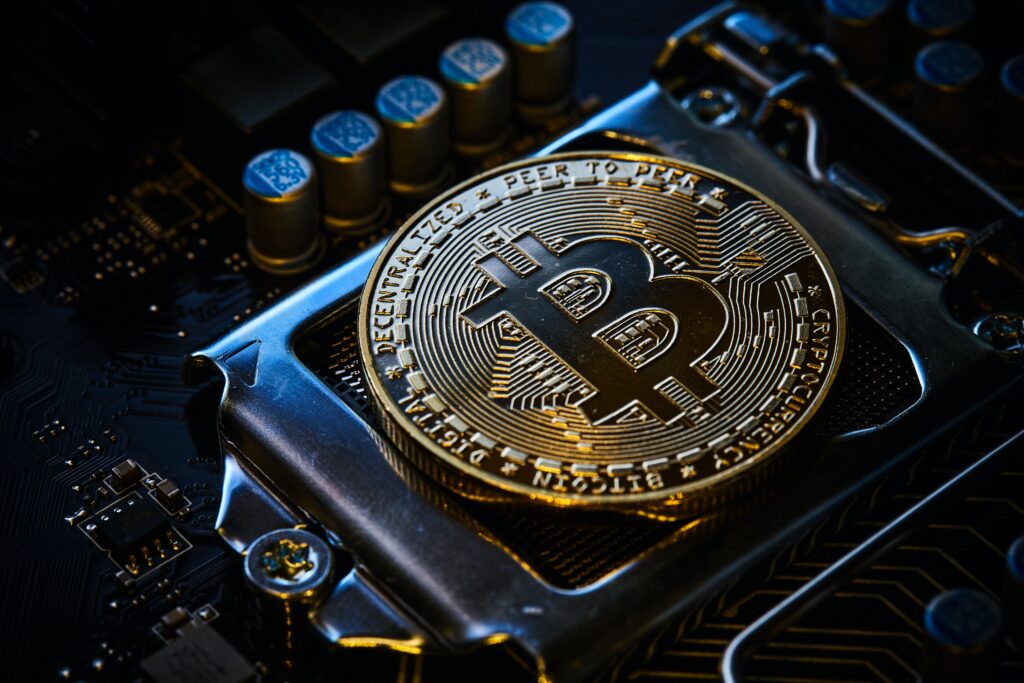
The buzz around the term ‘blockchain’ gained gargantuan momentum in recent years. Defined as a distributed, immutable ledger, this technology has revolutionized how the flow of transactions and assets worked traditionally. Several sectors have been engrossed in strategizing and contemplating the promised application of this technology. The banking and financial sector also did not lack behind in being a part of this revolution.
Blockchain posed better efficiency and transparency when compared to traditional record-keeping synonymous with financial institutions. Being decentralized in nature it made stakeholders in financial institutions have better trust relationships, transparency, and efficiency. Expediting transactions across geographies, increased security and transparency, alleviating human error, so and so forth, blockchain technology treasures transformational powers when it comes to the banking and finance sector.
Transforming record-keeping
Banks spend the majority of their operational costs and resources on record keeping entailing monetary business transactions, assessing assets-liabilities, profits, loss, etc. for a wide customer base. Banks traditionally have been centralized in their approach and invest a major expense into buying, maintaining, and security of these central databases, intermediary commission, and bookkeeping charges. With a large number of users and their subsequent transactions, record maintenance becomes an arduous task and ultimately leads to a longer processing time for payments. Thus, it is of utmost importance for banks to handle this bulk data with ease, security, and speed, all at the same time. With the availability of a tamper-proof ledger, blockchain makes it easier and more efficient for keeping track of ownership of such details. Being immutable in nature, data discrepancies are kept at bay with data stored with extensive security, authenticity, and accuracy. With the distinct mechanism of user authentication key for public and private users available in blockchain, wherein the transaction becomes visible to all users with a public key, but the transaction details being visible to users having the private key only, adds to the privacy feature at the same time maintains transparency. Employing Zero-Knowledge Proof Technology, blockchain aids in authenticating financial information without any sort of disclosure. This allows verification of user data without disclosing private information, thus preventing interception by unauthorized third parties.

Expediting transactions
Remittance flow worldwide accounts for hundreds of billions of dollars internationally every year. A $550 billion-dollar industry, remittances are a major source of wealth for low- and middle-income countries. Depending on the destination country and the type of service used, a remittance of couple of hundred dollars can incur an average fee between 5 percent and 9 percent. The cost incurred is mostly attributed to the compliances that have to be taken up for executing a remittance, starting from Know Your Customer (KYC), Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations, capital controls, exchange rates, so and so forth. From this cumbersome and expensive process, banks now save money and time by deploying blockchain technology for improving their remittance operations. For consumers too, with blockchain technology, transactions are expedited with much ease and with far less fee payment. Having a decentralized ledger, cryptocurrency gained popularity for remittance, lately. With the ability to avoid high costs charged by traditional banks, cryptocurrency is viewed as an attractive alternative for users to send money overseas. In 2021, remittances using cryptocurrencies grew by nearly 900 percent. Blockchain democratized the user base across borders and now, anyone can send payments and carry out transactions, regardless of an intermediary. Reports suggest that employing blockchain in banks will help them cut costs on cross-border payment transactions and save up to $27 Billion by 2030.
Friction-less Trade financing
Heavily relied on paperwork such as letters of credit and invoices., activities pertaining to trade financing are significantly slower in banks and traditional financial institutions. The current management systems are not equipped enough to readily execute a financial transaction to keep up with the trade volatility.
Blockchain proves to streamline this process with lesser paperwork, lower time consumption, and minimum regulations. With the feature of integration into a single digital document and real-time updates, blockchain technology can transform trade finance completely. With smart contracts equipped with computer protocols, transactions are quick with better accountability of all stakeholders thus, drastically reducing the fund management risk by increasing transparency.
Risk Management
Built on cryptographic standards of hash functions, private keys, and public keys, blockchain technology has immense potential to enhance security and fraud reduction for banks. In the past few years, banks globally have been targeted for cyber-attacks and financial crimes like bank account hacks, data leakage, and fraud. With quicker transactions allowing minimal time for intrusion by hackers and a decentralized ledger blockchain allows superior vigilance of prevalent frauds or risks. Many today agree conclusively that blockchain has a plethora of features to offer to the banking industry which can significantly revolutionize the traditional banking systems. For most of the features that blockchain has to offer, banks need to identify the opportunities, determine their feasibility and impact, and hence, employ the technology.





 Market Research
Market Research Consumer Research
Consumer Research Industry Research
Industry Research Market Entry Strategy
Market Entry Strategy Feasibility Studies
Feasibility Studies Product Research
Product Research Automobile & Mobility
Automobile & Mobility Banking and Finance
Banking and Finance Consumer Products & FMCG
Consumer Products & FMCG Ecommerce & Retail
Ecommerce & Retail Industry & Manufacturing
Industry & Manufacturing Government & Public Sector
Government & Public Sector Industry Associations
Industry Associations Technology & Software
Technology & Software Venture Capital & PE
Venture Capital & PE Consulting & Advisory
Consulting & Advisory India Entry Market Research
India Entry Market Research Innovation Consulting
Innovation Consulting KX Market Radar
KX Market Radar Business Model Development
Business Model Development Gen Z Navigator
Gen Z Navigator